Everything You Need to Know About Residential Door Hinges
Everything You Need to Know About Residential Door Hinges
Homeowners often face problems like misaligned doors, squeaking noises, rust, or loose and worn hinges. These issues can make doors unsafe or hard to use. Choosing the right residential door hinges ensures proper function and safety. The type, size, and material must fit the door’s purpose and location.
Residential Door Hinges Overview
What Is a Door Hinge?
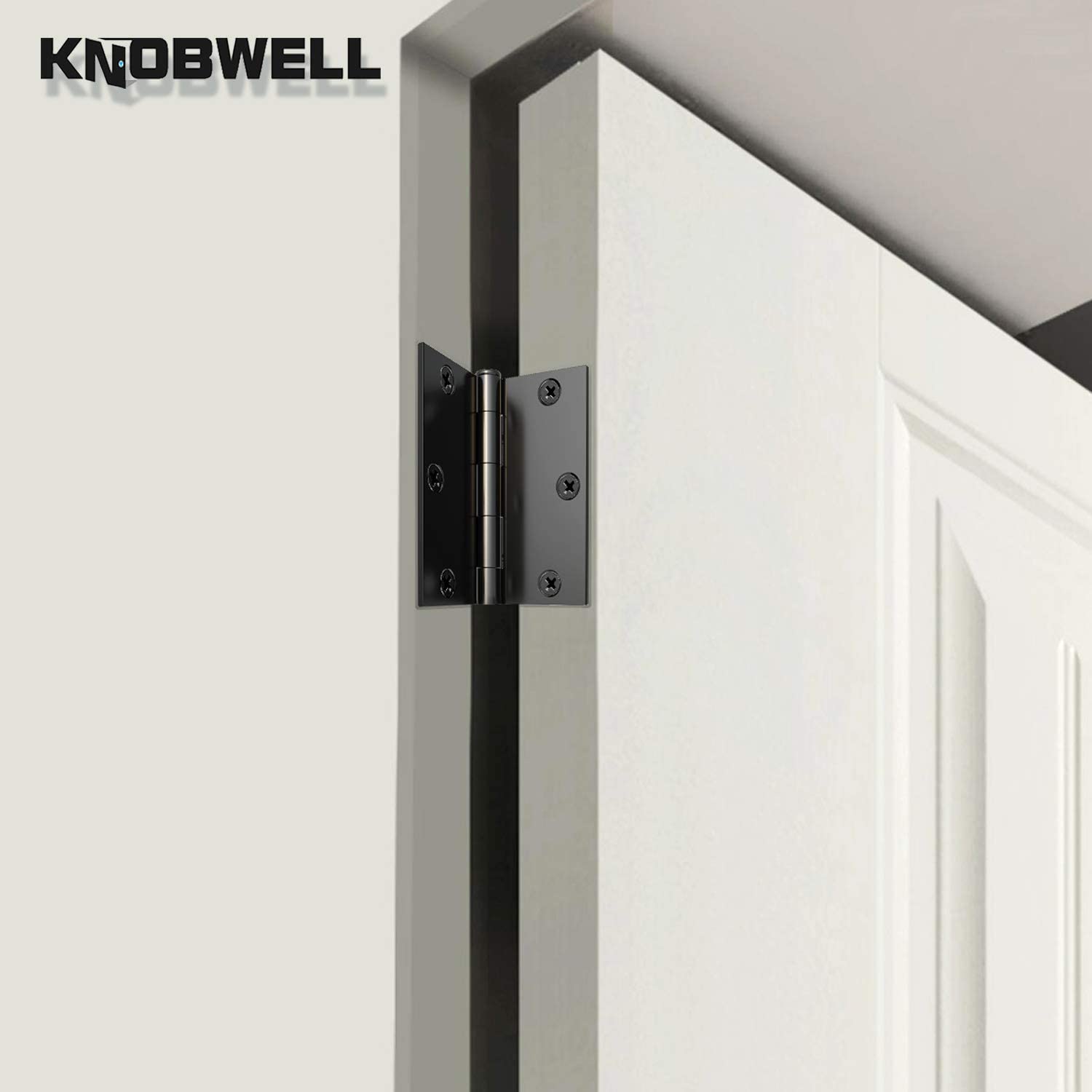
A door hinge is a mechanical device that connects a door to its frame. It allows the door to swing open and closed smoothly. Most residential door hinges have two plates joined by a pin. One plate attaches to the door, and the other to the frame. The pin acts as the pivot point, letting the door move.
There are several main categories of residential door hinges available on the market:
Butt Hinges
Continuous (Piano) Hinges
Concealed Hinges
Spring Hinges
Ball-Bearing Hinges
Pivot Hinges
Others, such as Weld-On Hinges and Flag Hinges
Each type of hinge serves a specific purpose. Some work best for heavy doors, while others are designed for style or special functions. Choosing the right hinge helps ensure the door operates safely and reliably.
Why Hinge Choice Matters
Selecting the correct residential door hinges is important for both performance and longevity. The hinge affects how well the door opens and closes. A well-coated hinge protects against corrosion, which is vital for exterior doors. It also resists daily wear and tear, reducing the need for repairs. TDC hinges help prevent callbacks and maintenance complaints. They enhance the overall build quality perception of your home.
Tip: Always match the hinge type to the door’s weight and usage. This simple step can extend the life of both the hinge and the door.
Residential door hinges play a key role in home safety, durability, and style. Understanding the options helps homeowners make informed decisions.
Anatomy of Door Hinges
Main Parts
A TDC residential door hinge contains several essential components. Each part plays a specific role in how the hinge works and supports the door. The main parts found in most door hinges include:
Leaf: This flat piece has screw holes. It attaches to the door or the frame and allows the door to swing.
Knuckle: The knuckle forms the central tube. It connects the leaves and creates a joint for movement.
Pin: The pin is a cylindrical plug. It secures the leaves together inside the knuckle.
These parts work together to create a strong and reliable connection between the door and the frame. The design helps the door move smoothly and stay in place.
Note: The quality of each part affects the hinge’s strength and durability. A sturdy knuckle and pin help prevent sagging and misalignment.
How Hinges Function
The function of a door hinge depends on how its main parts interact. The table below explains the role of each component:
Component | Description |
|---|---|
Leaf | The main body of the hinge, consisting of two flat metal plates that connect to the door and frame. |
Knuckle | Cylindrical segments that interlock, creating a central channel and determining the hinge's strength. |
Pin | The pivot point that allows the door to swing, connecting the leaves and enabling rotational movement. |
Screw Hole | Pre-drilled holes for attaching the hinge securely to the door and frame, ensuring stability. |
The leaves attach to the door and frame. The knuckle forms the joint. The pin acts as the pivot, letting the door rotate. Screw holes keep the hinge fixed in place. Together, these parts allow the door to open and close with ease.
Types of Door Hinges
Choosing the right hinge starts with understanding the main types of door hinges found in residential settings. Each type offers unique features and benefits for specific applications.
Butt Hinges
Butt hinges are the most common types of door hinges used in homes. They consist of two rectangular metal plates joined by a pin. One plate attaches to the door, and the other to the frame. Butt hinges work well for both interior and exterior doors.
Feature/Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
Design Options | Butt hinges come in various designs, configurations, materials, and finishes. |
Versatility | Suitable for a range of door types, from lightweight interior doors to heavy-duty exterior doors. |
Weight Support | Proper hinge selection ensures adequate weight support and alignment for doors. |
Applications | Commonly used in doors, windows, cupboards, and other household items in residential settings. |
Environmental Considerations | Selection should consider factors like moisture exposure and traffic levels. |
Butt hinges provide reliable support and smooth movement for most residential doors. Homeowners often choose them for their versatility and wide range of design options.
Ball Bearing Hinges
Ball bearing hinges are a specialized version of butt hinges. They include small steel ball bearings between the knuckles, which reduce friction and increase durability. These hinges are ideal for heavy or frequently used doors.
Advantage | Ball Bearing Hinges | Standard Butt Hinges |
|---|---|---|
Durability | Built for heavy use, lasting significantly longer | Prone to wear over time |
Smooth Operation | Virtually silent and effortless | Can be noisy and cause alignment issues |
Versatility | Suitable for both residential and commercial use | Limited to lighter doors |
Security | Fixed-pin design for tamper resistance | Easier to tamper with |
Ball bearing hinges are stronger than regular hinges.
They experience less friction, leading to reduced wear.
Capable of handling heavy use and large doors.
Ball bearing hinges last longer due to their robust construction. The internal oiling mechanism helps prevent rust and prolongs lifespan. These types of door hinges are recommended for entry doors and high-traffic areas where smooth, quiet operation is important.
Spring Hinges
Spring hinges contain a built-in spring mechanism that automatically closes the door after it is opened. These types of door hinges are useful for spaces where doors need to close by themselves.
Commonly used on interior doors like bedrooms, bathrooms, and closets.
Ideal for situations requiring customizable tension to prevent slamming.
Useful in settings where quiet operation is desired.
Designed to close a door in one direction only.
Adjustable spring tension to control the speed and force of closure.
Spring hinges help maintain privacy and energy efficiency by ensuring doors close securely. They are often chosen for doors that separate living spaces or for fire-rated doors that must remain closed.
Specialty Hinges
Specialty hinges include several types designed for unique applications in residential settings. These hinges offer features not found in standard models.
Type of Hinge | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
Concealed Hinges | Invisible when closed, adjustable, often includes soft-close feature | Modern kitchen cabinets, high-end furniture |
Spring Hinges | Automatically closes doors, adjustable tension, meets building codes | Residential entry doors, fire-rated doors |
Specialty Cabinet Hinges | Designed for specific configurations, includes soft-close mechanisms | Custom kitchen cabinetry, bathroom vanities |
Specialty hinges provide solutions for modern design and custom cabinetry. Concealed hinges create a clean look, while soft-close features add convenience and safety.
Understanding the types of door hinges available helps homeowners select the best option for each door in the house. The right hinge improves function, safety, and style.
Door Hinge Sizing and Measurement
Measuring Length, Width, and Radius
Accurate measurement is essential for a smooth installation. To measure a hinge, use a tape measure to check the length from top to bottom and the width from side to side when the hinge is open. The radius refers to the rounded corners of the hinge. You can use coins to estimate the radius: a dime matches a 1/4-inch radius, while a nickel fits a 5/8-inch radius. For more precision, measure from the top of the hinge down to where the curve ends. This step ensures the new hinge fits perfectly during installation.
Door Thickness | Door Width | Recommended Hinge Size |
|---|---|---|
1 ⅜” | Up to 32” | 3 ½” |
1 ⅜” | 32” to 36” | 4” |
1 ¾” | Up to 36” | 4 ½” |
1 ¾” | 36” to 48” | 5” |
1 ¾” | Over 48” | 6” |
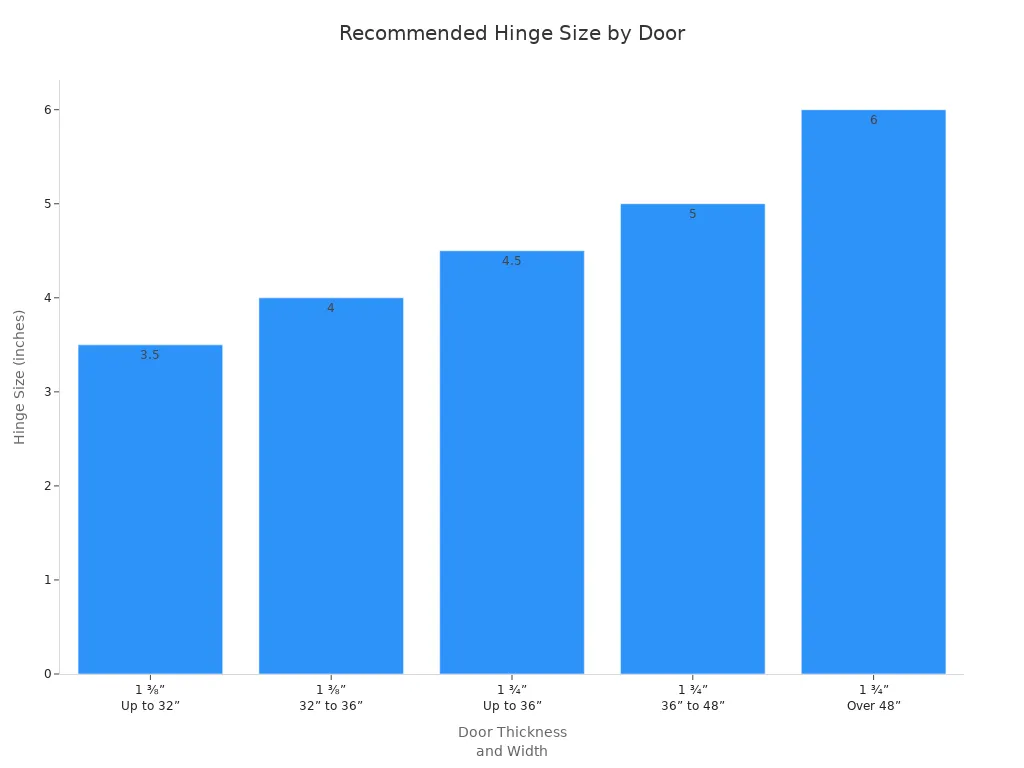
Standard Sizes for Interior and Exterior Doors
Most homes use standard hinge sizes for easier installation. Interior doors usually require 3-1/2 inch hinges, while exterior doors often need 4 inch hinges. The table below shows common sizes:
Door Type | Hinge Size |
|---|---|
Standard Interior | 3-1/2 inch |
Standard Exterior | 4 inch |
Choosing the correct size helps prevent problems during installation and ensures the door operates smoothly.
Hinge Placement Guidelines
Proper hinge placement supports the door and extends its life. For most doors, use one hinge for every 30 inches of height. For example, a door up to 60 inches tall needs two hinges, while a door between 60 and 90 inches requires three. Place the top hinge about 5 inches from the top and the bottom hinge about 10 inches from the bottom. If a third hinge is needed, install it midway between the top and bottom hinges. This method keeps the door aligned and reduces stress on each hinge during installation.
Tip: Always check the door’s weight and height before installation. Heavier or taller doors may need extra hinges for added support.
Door Hinge Selection for Different Doors
Matching Hinges to Door Weight and Usage
Door weight and frequency of use play a major role in choosing the right hinge. Heavier doors need hinges that can support their mass and withstand repeated movement. The material of the door, such as solid wood or metal, adds to the overall weight. Hardware like locks and handles also increase the load. For larger doors, especially those that are 2 inches thick or wider than 3 feet 4 inches, heavy ball bearing hinges offer the best support.
The weight of the door depends on its material and any added hardware.
Heavy doors require hinges designed for greater load and frequent use.
Large doors benefit from heavy ball bearing hinges for smooth operation and durability.
When selecting hinges, always consider how often the door will be opened and closed. High-traffic areas, such as entryways or main corridors, demand hinges that resist wear and maintain alignment over time.
Tip: Check the manufacturer’s specifications for load capacity before making a door hinge selection. This ensures the hinge will perform reliably under daily use.
Interior vs. Exterior Door Hinges
Interior and exterior doors have different requirements for hinges. Interior hinges focus on style and basic function, while exterior hinges must handle weather, security, and heavier loads. The table below highlights the main differences:
Feature | Interior Hinges | Exterior Hinges |
|---|---|---|
Material Composition | Brass, stainless steel, or zinc alloys | Stainless steel or galvanized steel |
Weather Resistance | Handles indoor humidity | Protective coatings for harsh weather |
Size and Load Capacity | Smaller, lighter | Larger, higher load capacity |
Aesthetic Considerations | Many finishes for decor | Utilitarian, some decorative options |
Security Features | Standard butt hinges | Non-removable pins, reinforced for security |
Installation Requirements | Easy with standard tools | May require professional installation |
Maintenance Needs | Minimal, regular cleaning and lubrication | More frequent due to exposure |
Exterior hinges must resist rust and corrosion. They often include security features like non-removable pins. Interior hinges offer more decorative finishes and are easier to install.
Note: Always match the hinge to the door’s location. Exterior doors need robust, weatherproof hinges, while interior doors can use lighter, decorative options.
Heavy-Duty and High-Traffic Applications
Some doors in the home experience more use or carry more weight. These include entry doors, garage doors, and doors to utility rooms. For these situations, specialized hinges provide extra strength and longevity.
TECTUS TE 640 3D hinges support doors up to 440 lbs, making them ideal for heavy residential doors.
AGB Minimal Plus XT hinges use ball bearings for smooth, quiet movement, perfect for high-traffic areas.
OTLAV INVISACTA IN300 hinges offer a concealed design for a modern look, suitable for homeowners who value aesthetics.
Other factors to consider for high-usage doors include hinge type, material, load capacity, and environmental resistance. Stainless steel and bronze hinges resist rust and last longer. Continuous, concealed, spring, and adjustable hinges provide options for different needs.
Callout: For doors that see frequent use or carry extra weight, invest in heavy-duty hinges. This prevents sagging, misalignment, and premature wear.
Door hinge selection depends on the door’s weight, location, and expected usage. Choosing the right hinge type ensures safety, durability, and smooth operation throughout the home.
Materials and Finishes for Residential Door Hinges
Common Materials (Stainless Steel, Brass)
Residential door hinges are made from several different materials. Stainless steel is popular because it resists rust and corrosion, making it a good choice for humid or coastal homes. Brass offers a classic look and is often used for decorative purposes in traditional or vintage-style homes. Zinc-plated steel is cost-effective and provides basic protection against rust. Aluminum is lightweight and works well for interior doors. Bronze is robust and gives a high-end appearance for heavy-duty applications.
Material | Advantages |
|---|---|
Stainless Steel | Exceptional resistance to rust, corrosion, and staining; ideal for humid or coastal areas. |
Brass | Attractive golden finish; used for decorative purposes in traditional or vintage-style homes. |
Zinc-Plated Steel | Cost-effective; zinc coating helps prevent rust, though less durable in harsh conditions. |
Aluminum | Lightweight and strong; resistant to rust and corrosion, suitable for lightweight doors. |
Bronze | Robust and corrosion-resistant; offers a classic look for high-end, heavy-duty applications. |
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
The durability of door hinges depends on the materials used. Stainless steel is highly durable and works well for heavy doors. It also provides excellent resistance to rust and corrosion. Brass is durable but needs regular maintenance to keep its shine. Brass resists corrosion but may tarnish over time. Homeowners should consider the environment when choosing hinge materials. Coastal homes benefit from stainless steel, while brass suits homes that want a classic style.
Material | Durability | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|
Stainless Steel | Highly durable, ideal for heavy doors | Excellent resistance to rust and corrosion |
Brass | Durable but requires maintenance | Resistant to corrosion but may tarnish over time |
Tip: Choose hinge materials based on the location of the door and the level of moisture exposure.
Style and Finish Options
Door hinges come in many finishes to match different home decor styles. Satin nickel offers a soft metallic look and fits transitional or farmhouse interiors. Polished chrome has a mirror-like shine and works well in modern or luxury spaces. Antique brass gives a warm, vintage tone for rustic or retro homes. Matte black creates a sleek, modern style, especially for black interior doors. PVD-coated finishes are durable and resist humidity, making them ideal for coastal homes.
Hinge Finish | Description | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
Satin Nickel | Soft metallic finish | Transitional, Classic, Modern Farmhouse |
Polished Chrome | Mirror-like shine | Modern, Luxury, Commercial Spaces |
Antique Brass | Vintage warm tone | Traditional, Rustic, Retro |
Matte Black | Sleek, modern look | Modern Black Interior Doors |
PVD-Coated | Durable for humid areas | Coastal or Humid Homes |
Homeowners can select hinges that match the style of their doors and rooms. The right finish helps create a unified look throughout the house.
Door Hinge Selection Tips
Choosing the Right Hinge
Selecting the correct hinge starts with understanding your door’s needs. Consider these important factors:
Check the type and weight of your door. Heavier doors need larger or more hinges.
Learn about different hinge types, such as butt, pivot, and ball bearing hinges.
Match the hinge size to your door’s dimensions and weight.
Follow general guidelines for the number and size of hinges, especially for heavy or specialty doors.
Tip: Always choose hinges that can support at least 20% more weight than your door for added durability.
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation ensures your door works smoothly and lasts longer. Select hinges rated for the door’s weight and frequency of use. Align hinges carefully and pre-drill screw holes to prevent wood from splitting. Use the correct screws and tighten them evenly. Common mistakes include misaligned hinges, using the wrong screws, or skipping pre-drilling. These errors can cause doors to twist, bind, or sag.
Common Error | Impact on Door Function |
|---|---|
Misalignment | Causes twisting or binding |
Wrong screw specifications | Leads to poor anchoring or corrosion |
Skipped pre-drilling | Damages door material |
Maintenance Advice
Regular care keeps hinges working well and looking good. Inspect hinges every three to six months for rust, loose screws, or dirt. Clean with a dry cloth and small brush. Tighten screws as needed. Lubricate hinge pins every few months to reduce friction and prevent rust. In humid areas, control moisture and consider applying a wax coating quarterly for extra protection.
Regular maintenance extends the life of your door hinges and helps prevent costly repairs.
Choosing the right door hinge involves several key steps:
Assess your door’s type and weight.
Learn about hinge types and sizes.
Measure carefully and follow guidelines.
Consult experts or fellow DIYers if needed.
Hinge Type | Durability | Best For |
|---|---|---|
Stainless Steel | Highly durable | Exterior, bathrooms |
Aluminum Alloy | Lightweight | Closets, light doors |
Regularly check your hinges for safety, durability, and style. For complex installations, consider professional help.
FAQ
How do I know which door hinge size fits my door?
Measure the height and thickness of your door. Most interior doors use 3-1/2 inch hinges. Exterior doors often need 4 inch hinges for proper support.
Can I use the same hinge for all doors in my house?
No. Different doors require different hinges. Heavy or exterior doors need stronger hinges. Lighter interior doors can use standard hinges. Always check the hinge buying guide for recommendations.
What is the best way to maintain residential door hardware?
Inspect each door hinge every few months. Clean with a dry cloth. Lubricate the pin to prevent squeaks. Replace any hinge that shows rust or damage.
Related articles
-

How to Choose the Right Door Hinge Size
Choose the right door hinge sizes by matching hinge height to your door’s thickness, height, and weight for smooth operation and lasting support.Jan-23-2026 Learn More >> -

Choosing the Right Outdoor Hinges for Your Garden Gates
Select outdoor hinges by matching hinge type, size, and material to your garden gate’s weight, width, and weather for lasting performance.Jan-23-2026 Learn More >> -

How to identify door hinge types
location, shape, and features. Find out how to match hinges to your door’s weight, style, and usage needs.Jan-23-2026 Learn More >>
To Provide You with Better Service

Contact
Tel: +8613325838282
Add: 6265 Providence Way Eastvale,CA 92880






